Road safety has become a top priority in the automotive industry, leading to the development of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). This technology enhances driving safety by assisting drivers in avoiding accidents and improving vehicle control. If your car is less than ten years old, it may already have some ADAS features.
This article explores what ADAS is, how it works, its key features, advantages, limitations, and its future in India.
What is ADAS?

ADAS stands for Advanced Driver Assistance System. It is a collection of smart safety features designed to assist drivers, reduce road accidents, and enhance overall driving safety. Using cameras, sensors, and radar technology, ADAS helps detect obstacles, monitor surroundings, and take corrective actions like automatic braking and lane assistance.
How Does ADAS Work?
ADAS uses multiple components to analyze real-time driving conditions and assist the driver accordingly.
Main Components of ADAS:
Radar Sensors: Detect objects at a distance and track their speed.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Creates detailed 3D maps for precise obstacle detection.
Cameras: Provide a 360-degree view and assist with lane and object recognition.
Ultrasonic Sensors: Help in close-range obstacle detection, such as during parking.
Onboard Computer: Processes data and takes appropriate actions like warning the driver or adjusting vehicle movements.
These components work together to prevent accidents, improve navigation, and enhance driver awareness.
Key Features of ADAS

ADAS includes several features that improve road safety and driving comfort.
Popular ADAS Features:
Feature
Function
Collision Avoidance System
Detects potential crashes and warns the driver.
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)
Applies brakes automatically to prevent accidents.
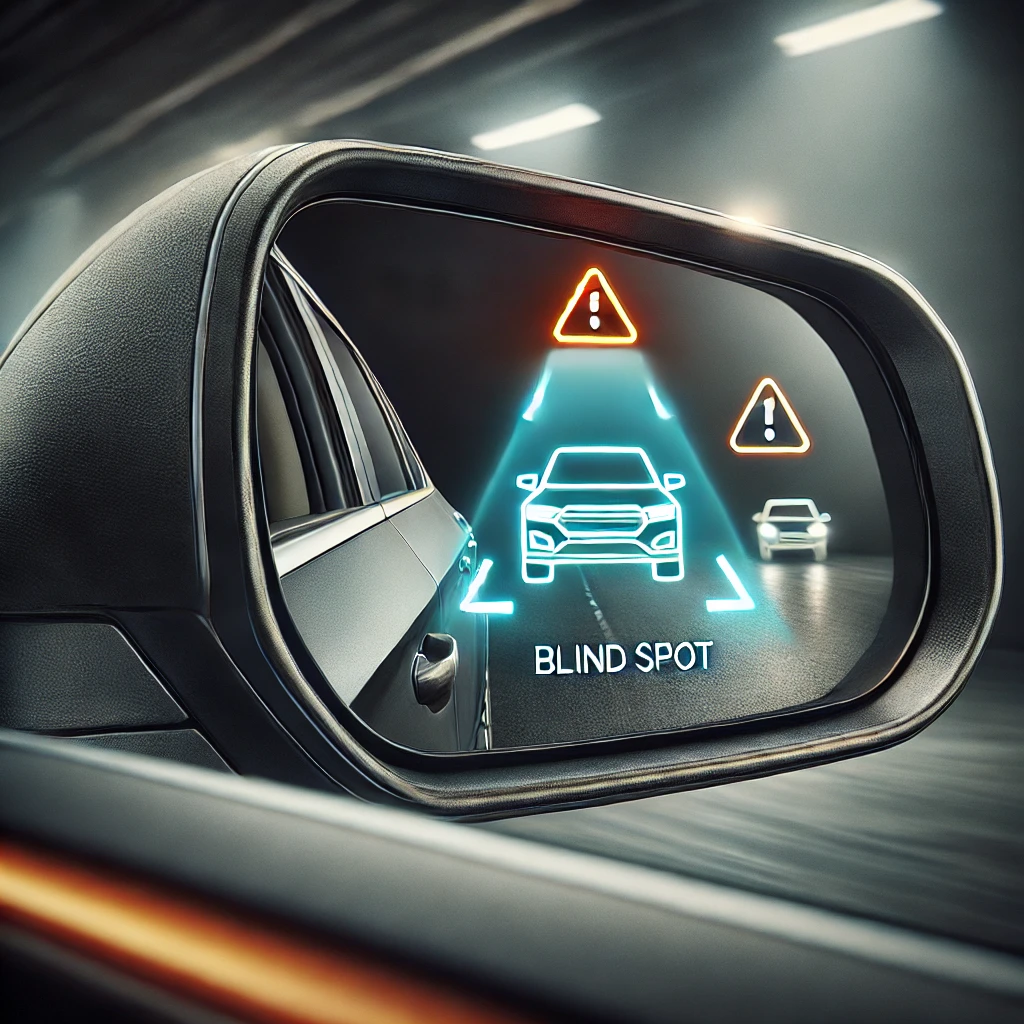
Blind Spot Monitoring
Alerts the driver about hidden vehicles in blind spots.
Lane Departure Warning
Notifies the driver if the car drifts out of its lane.
Adaptive Cruise Control
Adjusts vehicle speed based on traffic flow.
Driver Fatigue Detection
Identifies signs of tiredness and alerts the driver.
Traffic Sign Recognition
Reads road signs and informs the driver.
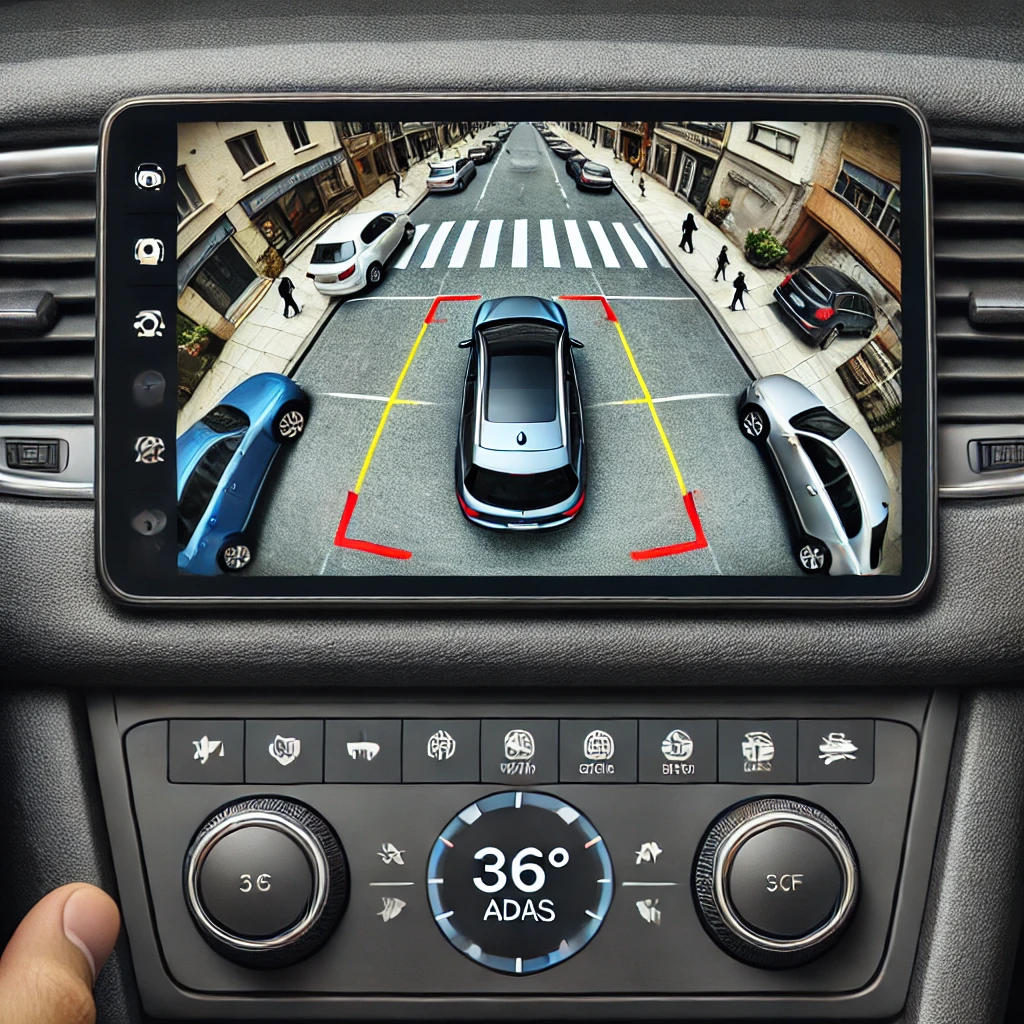
Parking Assistance
Aids in parking, sometimes handling it completely autonomously.
These features enhance safety, reduce human errors, and improve driving convenience.
Levels of ADAS Automation

The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) classifies ADAS into six levels, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (fully autonomous vehicles).
ADAS Automation Levels:
Level
Driver’s Role
Example Features
Level 0
Fully manual driving
Blind Spot Monitoring
Level 1
Partial driver assistance
Lane Keeping, Adaptive Cruise Control
Level 2
Hands-off in some situations
Traffic Jam Assist, Auto Parking
Level 3
Automated in some conditions, human intervention required
Highway Driving Assist
Level 4
Fully autonomous in specific environments
Self-Driving Taxis, Valet Parking
Level 5
Full autonomy, no driver needed
Completely self-driving cars
Currently, most ADAS-equipped cars in India operate at Level 2.
Benefits of ADAS

1. Enhanced Road Safety
ADAS helps prevent accidents by providing early warnings and automatic interventions like braking.
2. Less Driver Fatigue
Adaptive features such as Cruise Control and Lane Assist reduce stress during long drives.
3. Better Fuel Efficiency
ADAS improves driving efficiency, leading to better fuel economy and lower emissions.
4. Smart Parking Assistance
Parking sensors and automated parking systems make parking easier, even in tight spaces.
5. Improved Traffic Awareness
ADAS ensures better road discipline by assisting with speed limits and traffic signs.
Challenges of ADAS in India
Despite its advantages, ADAS faces several challenges on Indian roads.
1. Lack of Road Markings
Many roads lack clear lane markings, affecting features like Lane Keep Assist.
2. Unpredictable Traffic
India’s roads are filled with pedestrians, stray animals, and unpredictable drivers, making ADAS implementation difficult.
3. Weather Conditions
Rain, fog, and extreme sunlight can interfere with sensors and cameras, affecting their performance.
4. Data Processing Limitations
ADAS relies on fast and accurate data processing, and any error can lead to incorrect warnings.
5. Legal and Liability Issues
Who is responsible if an ADAS-equipped car is involved in an accident? Legal regulations on driver responsibility are still unclear.
Future of ADAS in India

For ADAS to become mainstream in India, the following developments are essential:
Improved Road Infrastructure: Well-marked lanes and properly maintained roads.
Advanced AI Technology: Smarter ADAS systems that adapt to Indian traffic conditions.
Government Policies: Clearer laws regarding ADAS usage and liability.
Affordable ADAS Features: Cost-effective solutions for budget-friendly cars.
As India moves towards smart mobility and autonomous driving, ADAS adoption is expected to increase significantly in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about ADAS
1. What does ADAS stand for?
ADAS stands for Advanced Driver Assistance System.
2. Which Indian cars come with ADAS?
Some popular ADAS-equipped cars in India include:
Mahindra XUV700
Hyundai Tucson
MG Astor
Honda City e:HEV
Kia EV6
3. Can ADAS completely prevent accidents?
No, ADAS reduces accident risks but does not eliminate them. Drivers must always remain alert.
4. How does LiDAR help ADAS?
LiDAR helps detect obstacles and create 3D maps for better navigation and safety.
5. What is the future of ADAS in India?
With better infrastructure and AI advancements, ADAS adoption is expected to grow significantly.
Conclusion
ADAS is transforming vehicle safety and improving driving experiences worldwide. While challenges exist in India, the future of ADAS looks promising. With better infrastructure, smarter AI, and regulatory improvements, ADAS will play a vital role in making Indian roads safer and more efficient.