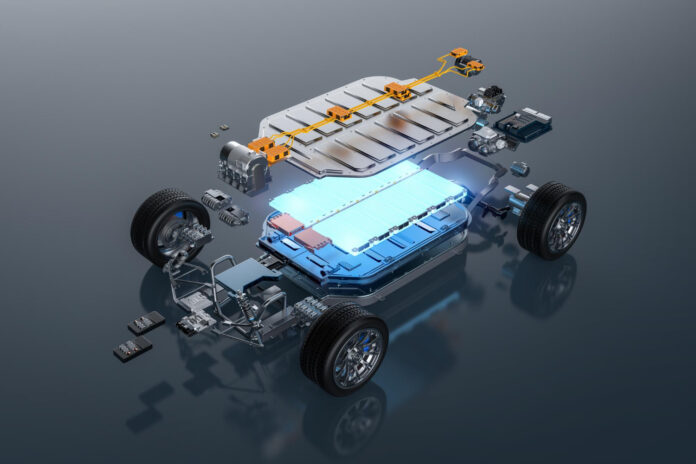
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming an increasingly popular choice for drivers looking to embrace a greener future, but have you ever wondered what makes them tick? At the heart of every electric vehicle lies its battery. EV batteries are fundamentally different from traditional car batteries and play a vital role in powering your vehicle efficiently. Whether you’re new to the world of electric vehicles or just curious about how EV batteries work, this guide will break down the essential concepts in simple terms. From how they store and release energy to the various types of batteries used, we’ll help you understand the technology that makes your EV run smoothly.
Key Points
- What’s an EV Battery?
- Inside the Battery: Cells, Modules, and Packs
- How It Stores Energy
- Charging Up
- Discharging: Powering Your Ride
- Battery Management System (BMS)
What’s an EV Battery?

The EV battery is like the petrol tank of a traditional car, but instead of guzzling petrol, it slurps up electricity. It’s the big, beefy power source that drives the electric motor, lights, and even the fancy touchscreen in your EV. Most EVs in 2025 use lithium-ion batteries because they’re lightweight, powerful, and can hold a ton of energy. Think of it as a giant rechargeable AA battery, but way cooler and packed with enough juice to haul you hundreds of kilometers. It’s the unsung hero that makes gas stations a distant memory!
Types of Batteries Used in Electric Vehicles
Inside the Battery: Cells, Modules, and Packs
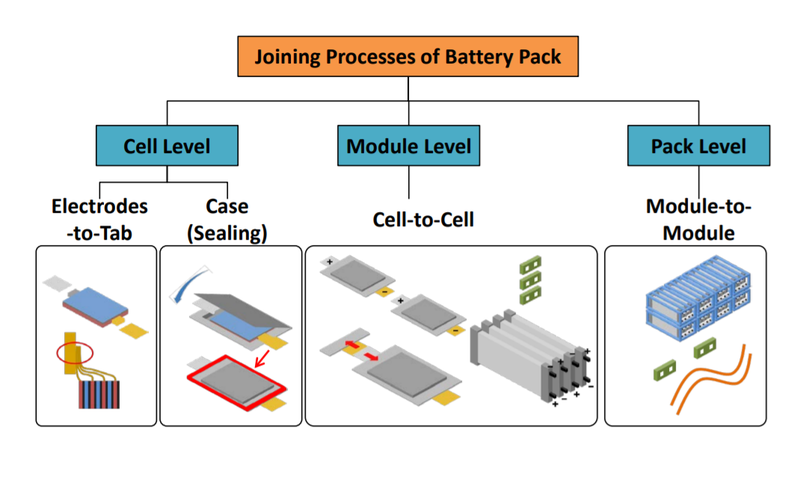
Let’s crack it open (not literally!). An EV battery isn’t just one big blob it’s a team effort. At the smallest level, you’ve got cells, tiny cylinders or pouches (like AA batteries on steroids) that store energy. A bunch of these cells are wired together into modules, kind of like Lego bricks stacked neatly. Then, several modules are bundled into a battery pack, the massive unit bolted under your car’s floor. This pack isn’t just cells it’s got cooling systems, wiring, and armor to keep everything safe. It’s like a perfectly organized city of power, buzzing under your feet!
How It Stores Energy
The magic happens. Inside each cell, there’s a dance between two key players: the cathode (positive side) and the anode (negative side), separated by an electrolyte goo. When you charge the battery, lithium ions shimmy from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte, storing energy like a coiled spring. The materials? Usually a mix of lithium, nickel, and cobalt for the cathode, and graphite for the anode. It’s like a microscopic energy hoarder quietly packing away power until you need it. No explosions, just pure chemical teamwork!
Charging Up

Plugging in your EV is like feeding it a big electric meal. When you hook up to a charger whether it’s a slow home plug or a zippy DC fast charger electricity flows into the battery. Those lithium ions boogie back from the anode to the cathode, reversing the dance and filling the battery with energy. A full charge might take 8 hours at home or 30 minutes at a fast station, depending on the setup. some 2025 EVs even sip power wirelessly via induction pads talk about futuristic! It’s like recharging your phone, but for a beast that weighs two tons.
Discharging: Powering Your Ride
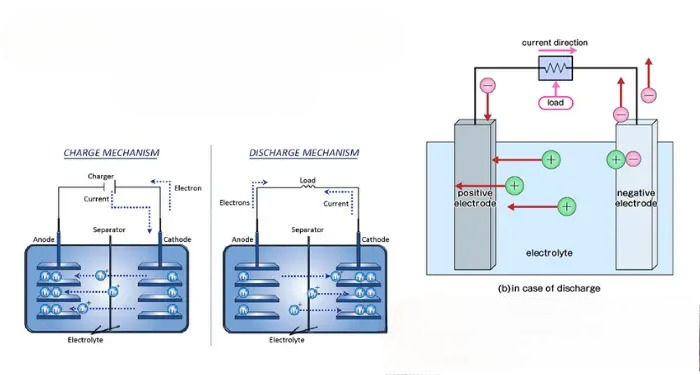
When you hit the accelerator, the battery discharges, sending those lithium ions racing back from the cathode to the anode. This flow creates an electric current that zaps through wires to the electric motor, spinning the wheels and propelling you forward. No gas, no noise just smooth, instant torque. The harder you push, the faster the ions move, draining the battery bit by bit. It’s like unleashing a herd of tiny electric horses, galloping to get you where you’re going!
Battery Management System (BMS)
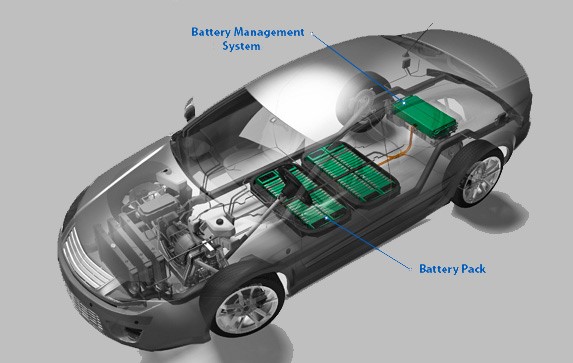
Meet the unsung genius: the Battery Management System (BMS). This little computer keeps the battery happy and healthy. It monitors temperature (too hot? It cranks the cooling!), balances the charge across cells (no slackers allowed!), and prevents overcharging or deep draining. Think of it as a strict babysitter watching every cell, tweaking the flow, and even telling your dashboard how much range you’ve got left. Without the BMS, your battery would be a chaotic mess. It’s the brain that turns raw power into a reliable road trip buddy!
Conclusion
Understanding how EV batteries work is crucial if you’re considering making the switch to electric driving. These batteries power your vehicle in an efficient, environmentally-friendly way, helping reduce emissions and the reliance on fossil fuels. How EV Batteries Work With advancements in battery technology, the future of electric vehicles looks bright. As EVs become more widespread, the performance and longevity of their batteries will continue to improve, offering drivers a sustainable and exciting alternative to traditional petrol-powered cars.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long do EV batteries last?
EV batteries are built to last! Most lithium-ion batteries in 2025 EVs come with warranties for 8-10 years or 150,000-200,000 kilometers. With proper care (like avoiding constant fast charging), they can even outlive that. Think of them like a trusty old phone eventually, they lose some pep, but they’ll stick around for years!
2. Can EV batteries be recycled?
Yep, they sure can! By 2025, recycling tech is booming companies break down old batteries to reuse lithium, cobalt, and other goodies. It’s like giving your EV battery a second life, cutting waste and mining needs. Some brands even aim for “closed-loop” systems where new batteries come from old ones. Pretty eco-cool, right?
3. Do EV batteries work in extreme weather?
They do, but they’re a bit picky. Cold weather slows the ion dance, cutting range by 10-20%, while scorching heat can stress the cells over time. The BMS helps by managing temps, and some EVs have liquid cooling or heaters. It’s like dressing your battery for the season keep it comfy, and it’ll perform!
4. How safe are EV batteries?
Super safe, thanks to tons of safeguards! The BMS prevents overcharging, and packs are built with crash-proof casings. Fires are rare stats show EVs catch fire less often than gas cars. It’s like having a high-tech vault under your car secure, sturdy, and ready for the road!







